Cloud Create
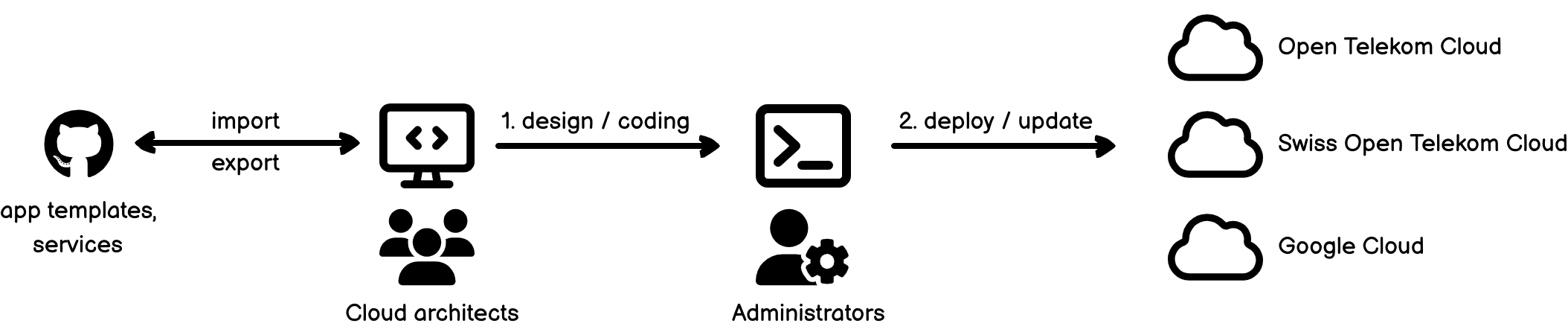
Cloud Create is a free-to-use Development and Management Platform, which enables cloud developers to create applications on Open Telekom Cloud fast.
- Cloud architects create applications from premade templates.
- They can visually design and adjust the application to fit their needs.
- An administrator deploys and updates the application on Open Telekom Cloud.
- Cloud architects can save a design as a private template for personal use or share it public with other users.
Figure 1. Overview
- Cloud architects and administrators can be the same user.
- Deployment on Swiss Open Telekom Cloud and the function "Save & Share templates" are upcoming features.
How cloud architects design the application
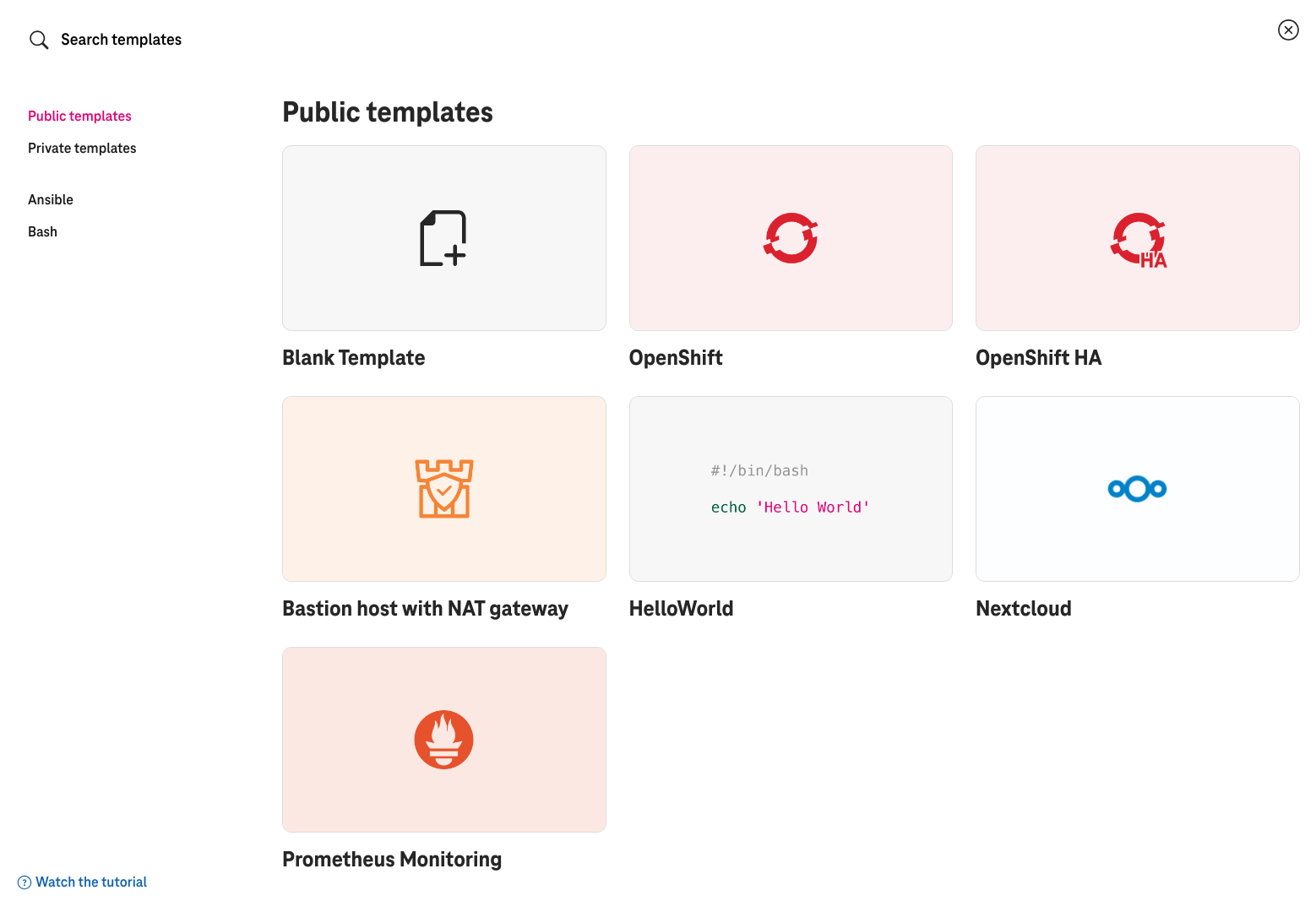
Cloud architects can design the application from scratch or from premade templates:
Figure 2. Select an app template to start.
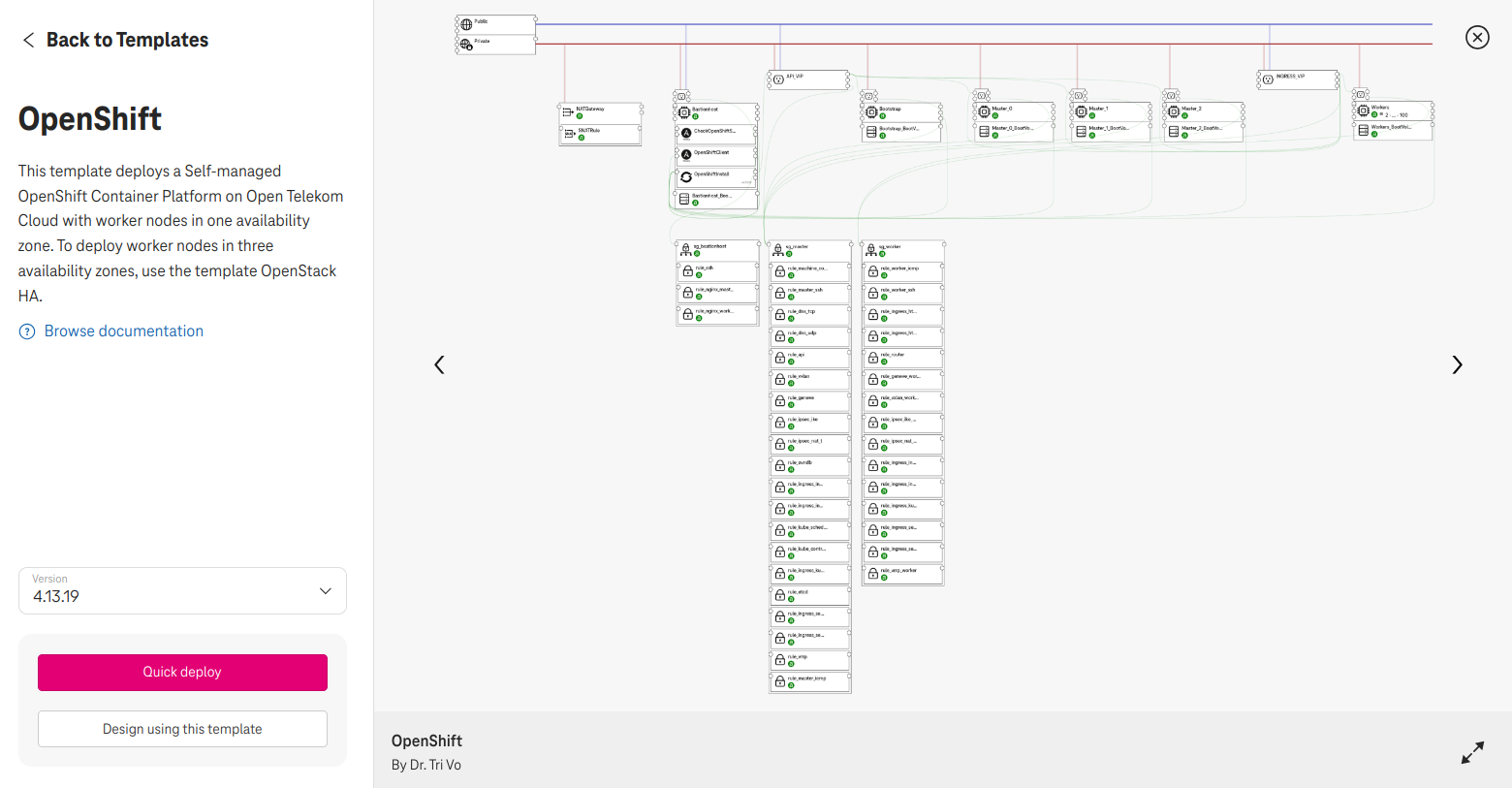
They can quickly deploy a template or start a new design from it:
Figure 3. Quick deploy OpenShift or Design using this template.
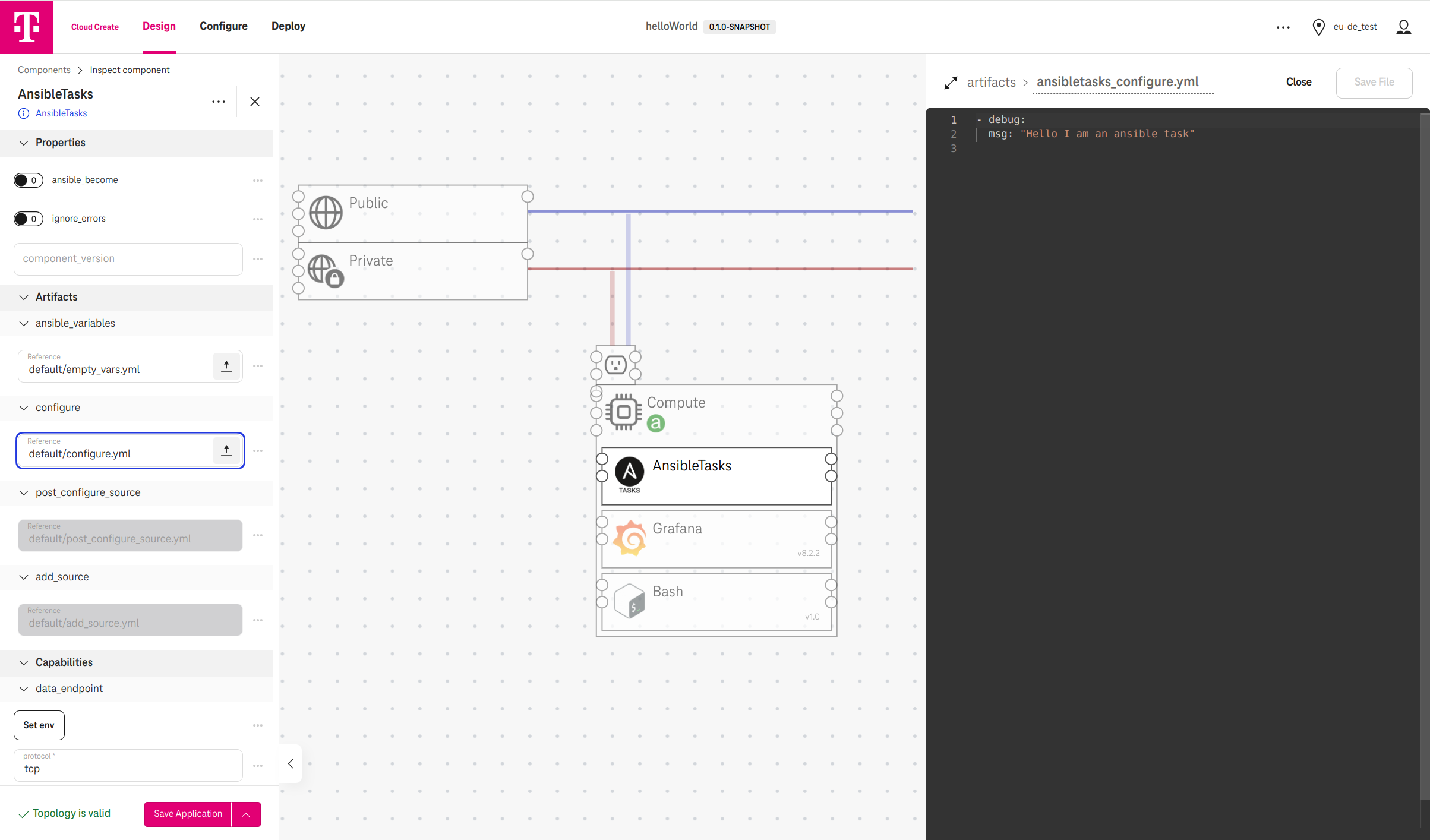
Cloud Create also comes up with a visual designer for less-coding or no-coding. Developers can drag and drop the components together like lego bricks as in the following example:
Figure 4. An application example with network, compute, ansible, bash scripts, and Grafana component.
- In the above example, the network and compute are infrastructure components. AnsibleTasks, Bash, and Grafana are service components.
- By using the Ansible and Bash components, developers can write code to execute on a compute directly.
- Grafana is an example of a ready-to-use service available in the designer. Developers can define new services and import them to the designer as well. More details on Section How to define and import and a new service.
App templates and service components are opensource and available on our Github.
How administrators deploy the application
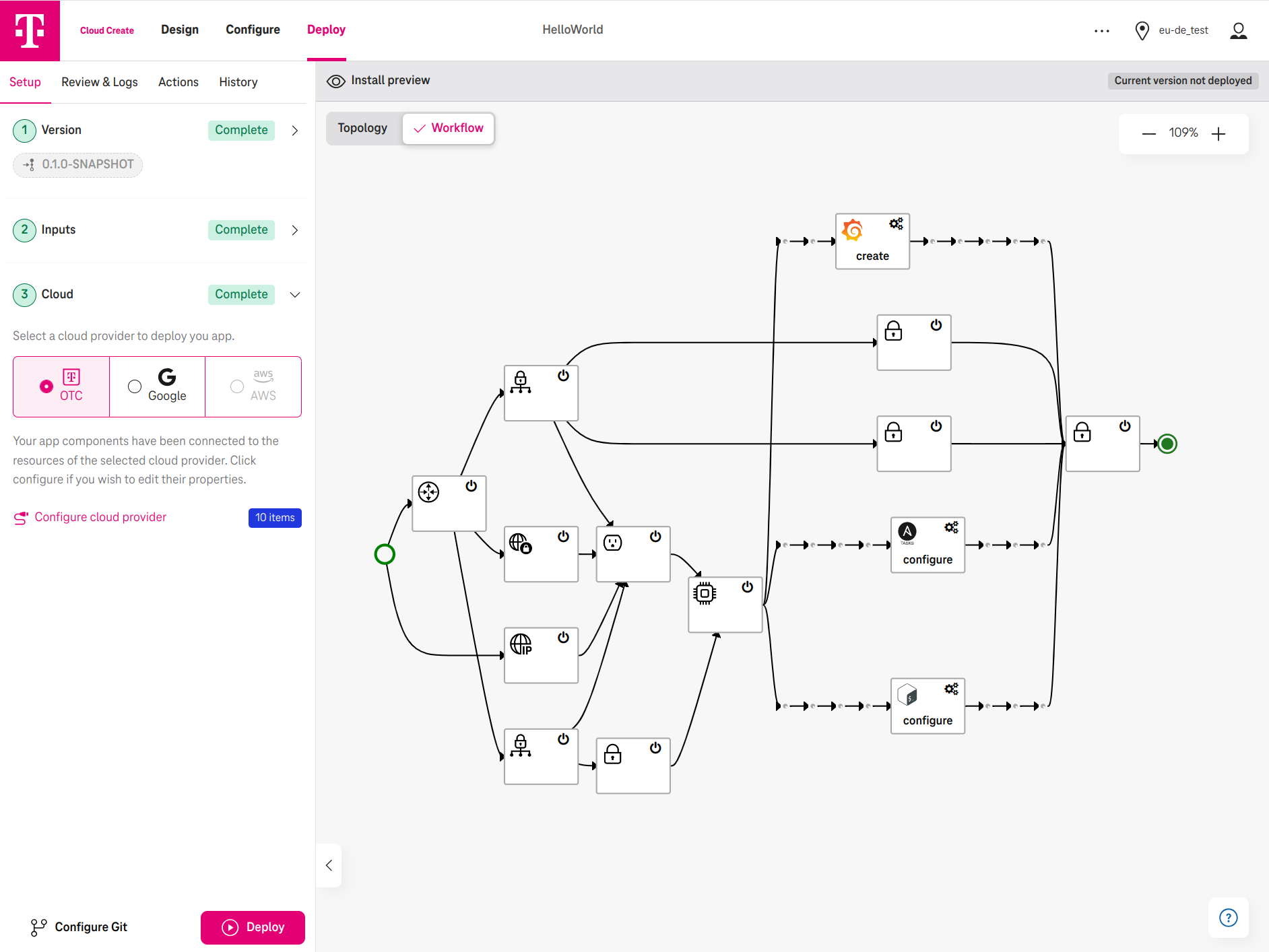
Before the deployment can start, administrators select a Version, provide Inputs, which were designed by the cloud architects, and select a cloud provider (e.g., Open Telekom Cloud) to deploy. In addition, administrators can review the auto-generated workflow before it starts.
Figure 5. Administrators select Open Telekom Cloud (OTC) to deploy
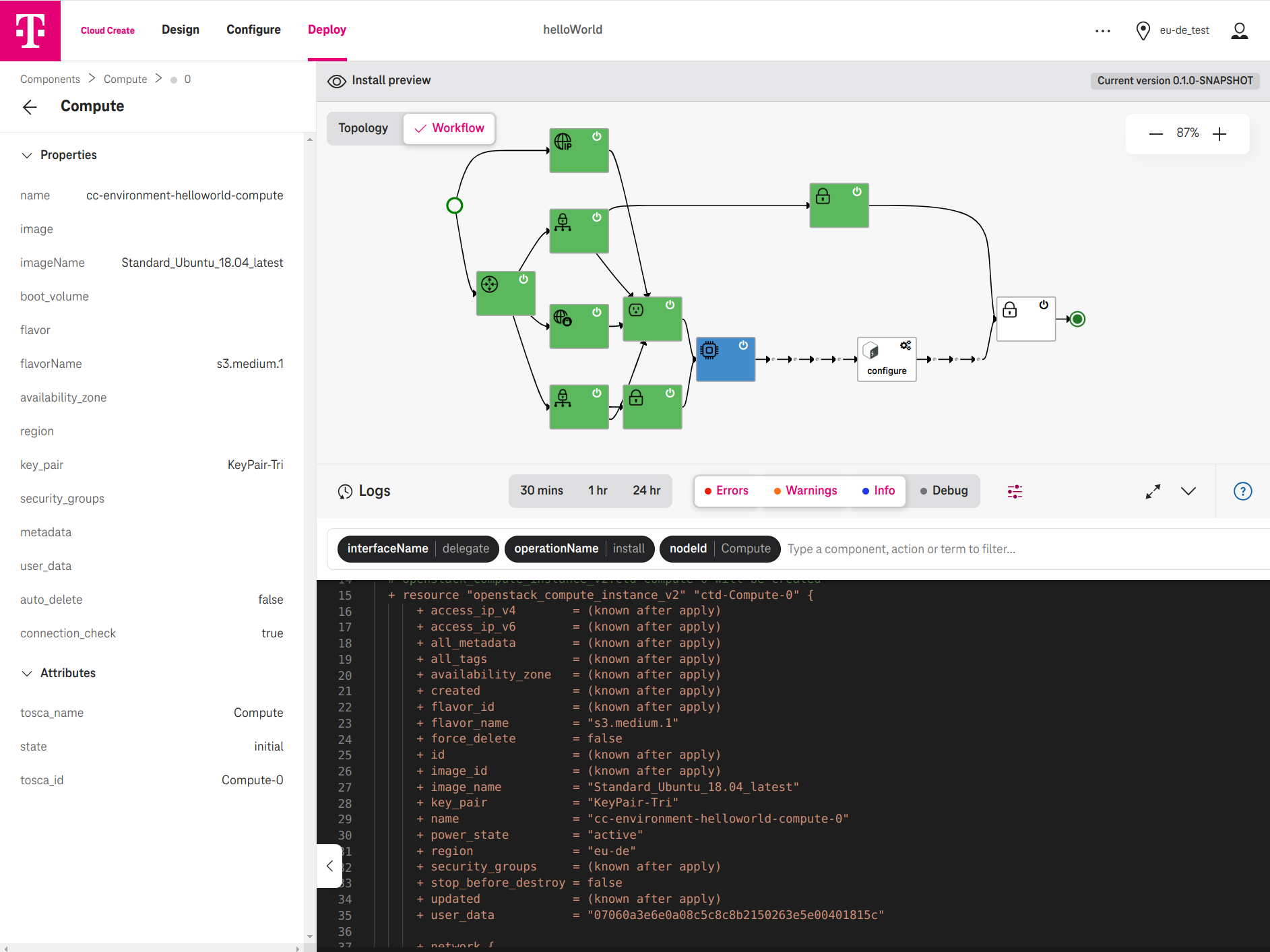
During the deployment, administrators can interactively click on a workflow step and see Terraform is applied for the infrastructure components. For the service components, the deployment script of the service (e.g., Ansible) is applied on the target compute.
Figure 6. An example Terraform is generated and applied for a Compute
Why Cloud Create?
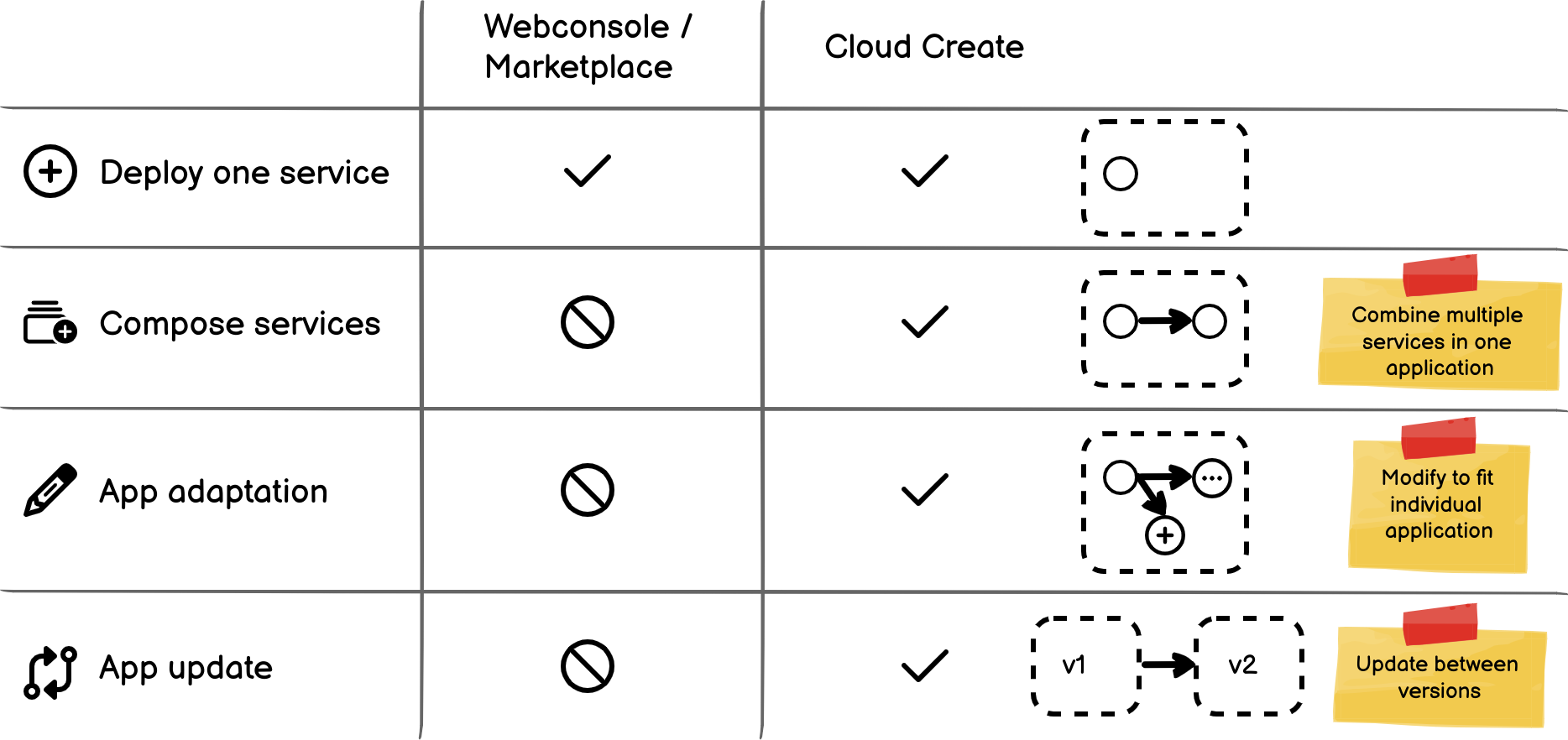
The following table shows the differences between the Web console / other tools and Cloud Create:
Figure 7. Features comparison
Both the Web console and Cloud Create can deploy one cloud service. However, an application nowadays consists of multiple cloud services but not just one. Furthermore, each application has individual needs to adapt to the cloud differently. The Web console can bring up one service up and running separately but cannot automate an application with multiple services.
With Cloud Create, after creating an application from a template, you can modify the application to fit your individual needs. For example, one of our customer used Cloud Create to create their application from the OpenShift template, then they added a worker node with the GPU capability and wrote an Ansible script to deploy packages on the bastion host, etc. The given example shows that the modification can happen in every corner, from the cloud infrastructure to the software layer of your application. Finally, you can run update between versions on operation day 2 as well. To update between versions, Cloud Create auto-calculates the differences between the two versions and auto-generates the update workflow steps from one version to other one.
New features
OpenShift template (v2.13)
Users can create a Self-managed OpenShift Container Platform on Open Telekom Cloud from the OpenShift template.
FAQ
What are the differences between Cloud Create and the Web console
With the Web console, users can only create the cloud infrastructure manually. It means, they can create a network, a storage, a VM separately but without automation.
On the other hand, Cloud Create enables developers to design and automate the deployment of the whole application including the cloud infrastructure and services. In addition, developers can design the application in various versions and run update between them. Finally, Cloud Create provides premade templates (e.g., OpenShift) to re-use and extend.
How can I login in to Cloud Create
You can log in to Cloud Create using an IAM user account with the Tenant Administrator role. This is the same credentials when you log in to the web console, not the ICU account.
If you do not have a user account in the IAM, see How to create a user account & login.
Which components are supported
An overview of all supported components is available in Section Components overview.
Is Cloud Create opensource
Cloud Create is based on two opensource projects Application Lifecycle Enablement for Cloud (Alien4cloud) and Ystia Orchestrator (Yorc). At Open Telekom Cloud, we further integrate it with OpenStack and Google Cloud, provide an easy-to-use UI, added features (e.g., secrets management, deployment update, OpenShift template, etc.), and enforce the strictest Privacy and Security Assessment (PSA) process of Deutsche Telekom.
All premade templates and service components are opensource and available on our Github. You can create pull requests to add more components and fix bugs.
Which Terraform version do you use
We use Terraform 1.5.4 under the Mozilla Public License v2.0 (MPL 2.0).