Configuring Private Domain Names for ECSs
If one of your ECSs is not working normally and you need to use the backup ECS to handle requests, but you have not configured private zones for the two ECSs, you need to change the private IP address in the code for the faulty ECS. This will interrupt your services and cause you to publish your website again, which is time- and labor-consuming.
Assume that you have configured private zones for the ECSs and have included their private domain names in the code. If one ECS is malfunctioning, you only need to change the DNS records to direct traffic to a normal ECS. Your services will not be interrupted, and you do not need to publish the website again.
Solution Design
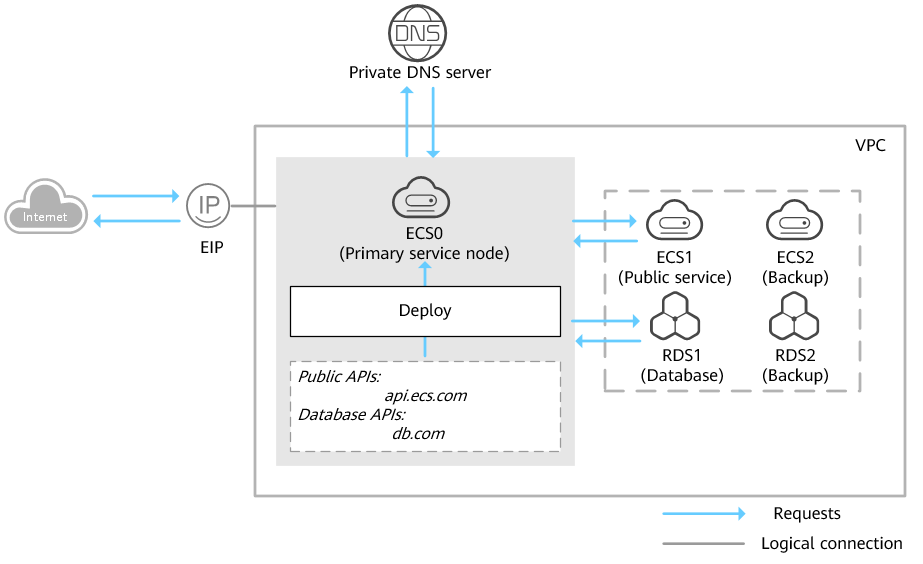
The figure below shows the networking of a website where ECSs and RDS instances are deployed in a VPC.
- ECS0: primary service node
- ECS1: public service node -> ECS2: backup service node
- RDS1: service database -> RDS2: backup database
- Higher efficiency and security: You can use private domain names to access ECSs in the VPCs, without going through the Internet.
- Easier management: Compared with IP addresses, domain names are easier to modify in the code. When an ECS is changed, you only need to change the DNS records without modifying the code.
Prerequisites
This table lists private zones and record sets planned for the cloud servers.
| Resource | Private Zone | Associated | Private IP | Record Set Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECS1 | api.ecs.com | VPC_001 | 192.168.2.8 | A | Public service node |
| ECS2 | api.ecs.com | VPC_001 | 192.168.3.8 | A | Backup for the public service node |
| RDS1 | db.com | VPC_001 | 192.168.2.5 | A | Service database |
| RDS2 | db.com | VPC_001 | 192.168.3.5 | A | Backup database |
Table 1 Private zones and record sets for each server
| Region | Service | Resource | Description | Quantity | Monthly Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eu-de | VPC | VPC_001 | The DNS server addresses must be the same as the private DNS server addresses of Open Telekom Cloud. For details, see Availability of secondary DNS | 1 | Free |
| ECS | ECS0 ECS1 ECS2 | Private domain name: api.ecs.com Associated VPC: VPC_001 ECS1: public service node Private IP address: 192.168.2.8 ECS2: backup service node Private IP address: 192.168.3.8 | 3 | For details, see ECS Product Pricing Details. | |
| RDS | RDS1 RDS2 | Private domain name: db.com Associated VPC: VPC_001 RDS1: service database Private IP address: 192.168.2.5 RDS2: backup database Private IP address: 192.168.3.5 | 2 | For details, see RDS Product Pricing Details. | |
| DNS | api.ecs.com db.com | api.ecs.com: Associated VPC: VPC_001 Record set type: A Value: 192.168.2.8 db.com: Associated VPC: VPC_001 Record set type: A Value: 192.168.2.5 | 2 | Free |
Table 2 Resource planning
Configuring Private Zones
Summary
The figure below shows the process for configuring private zones:
- (Optional) Create a VPC and a subnet on the VPC console. This operation is required when you are configuring private domain names for servers during website deployment.
- Create private zones and associate them with the VPC and add a record set to each private zone on the DNS console.
- (Optional) Change the DNS server addresses of the VPC subnet on the VPC console. This operation is required when you are configuring private domain names for servers where your website is running.
Procedure
-
(Optional) Create a VPC and a subnet.
Before configuring private domain names for the ECSs and databases required by your website, you need to create a VPC and a subnet.
a. Log in to the management console.
b. Click
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
c. Choose Network -> Virtual Private Cloud.
d. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Virtual Private Cloud.
e. Click Create VPC and configure the parameters based on
Table 3 <dns_bestprac_0002__table65603559163645>f. Click Create Now.
-
Create private zones.
Create private zones for the domain names used by ECS1 and RDS1.
a. Choose Network -> Domain Name Service.
The DNS console is displayed.
b. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Private Zones.
c. Click Create Private Zone.
d. Configure the parameters based on
e. Click OK. Then check the private zone created for
api.ecs.com.You can view details about this private zone on the Private Zones page.
noteClick the domain name to view SOA and NS record sets automatically generated for the zone.
- The SOA record set identifies the base DNS information about the domain name.
- The NS record set defines authoritative DNS servers for the domain name.
f. Repeat steps to create a private zone for
db.com. -
Add a record set to each private zone.
Add record sets to translate private domain names to private IP addresses of ECS1 and RDS1.
a. Click the domain name.
The record set page is displayed.
b. Click Add Record Set.
c. Configure the parameters
d. Click OK. An A record set is added for
api.ecs.com.e. Repeat steps to add an A record set for
db.com.Set the record set value of
db.comto192.168.2.5. -
(Optional) Change the DNS server addresses of the VPC subnet.
After you configure private domain names for nodes in the website application, you need to change the DNS servers of the VPC subnet to those provided by the DNS service so that the domain names can be resolved.
-
Switch to the backup ECS.
When ECS1 becomes faulty, you can switch services to ECS2 by changing the value of the record set added to private zone
api.ecs.com.a. Log in to the management console.
b. Click
in the upper left and select eu-de.
c. Choose Network -> Domain Name Service.
The DNS console is displayed.
d. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Private Zones.
e. In the private zone list, click the name of the zone
api.ecs.com.f. Locate the A record set and click Modify under Operation.
g. Change the value to
192.168.3.8.h. Click OK.
Traffic to ECS1 will be directed to ECS2 by the private DNS server.