Unsupported VPC Peering Configurations
The VPC peering connection configurations that are not supported in Open Telekom Cloud, are listed in the table below:
| Scenario | Example |
|---|---|
| If VPCs with the same CIDR block also include subnets that overlap, VPC peering connections are not usable. If two VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks but some of their subnets do not overlap, you cannot create a VPC peering connection to connect specific subnets that do not overlap. | Invalid VPC Peering for Overlapping: VPC CIDR Blocks VPCs with the same CIDR block also include subnets that overlap. Two VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks but some of their subnets do not overlap. |
| VPC peering connections cannot enable ECSs in their VPCs to share an EIP to access the Internet. If VPC-A and VPC-B are peered and ECS-A01 in VPC-A has an EIP, ECS-B01 in VPC-B cannot access the Internet using the EIP bound to ECS-A01. | Invalid VPC Peering for Sharing an EIP |
Table 1 Scenarios that VPC peering connections are invalid
Notes and Constraints
-
If the ECSs in VPCs connected by a VPC peering connections are in different security groups, you need to add rules to the security groups to allow access to each other. For details, Enabling ECSs in Different Security Groups to Communicate with Each Other Through an Internal Network.
noteIn all examples in this section, the ECSs in local and peer VPCs are in the same security group. No additional security group rule is required.
-
Each route table of a VPC can have a maximum of 200 routes. If you want to establish VPC peering connections between multiple VPCs, consider this restriction when planning networking.
-
In a VPC route table, the route priority is as follows:
-
Local route: A route that is automatically added by the system for communication within a VPC. It has a higher priority than a custom route.
-
Custom route: A route added by a user. It uses the longest prefix match rule to find a destination for packet forwarding.
-
Invalid VPC Peering for Overlapping VPC CIDR Blocks
If two VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks, the VPC peering connection may not take effect due to route conflicts. The following describes the reasons and configuration suggestions.
-
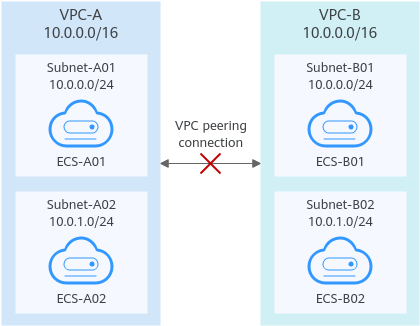
VPCs with the same CIDR block also include subnets that overlap.
VPC peering connections are not usable. As shown in Table 2, VPC-A and VPC-B, and their subnets have the same CIDR block. If you create a VPC peering connection between VPC-A and VPC-B, their route tables are shown in Table 2.
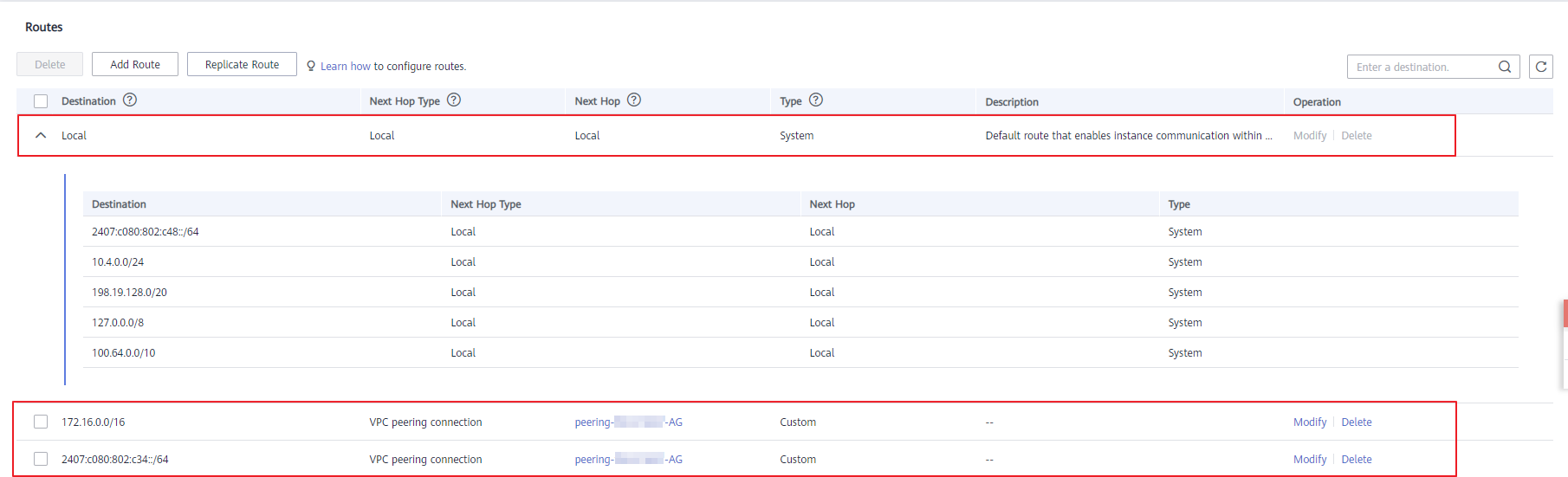
In the rtb-VPC-A route table, the custom route for routing traffic from VPC-A to VPC-B and the local route have overlapping destinations. The local route has a higher priority and traffic will be forwarded within VPC-A and cannot reach VPC-B.
Route Table Destination Next Hop Route Type Description rtb-VPC-A 10.0.0.0/24 Local System Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. 10.0.1.0/24 Local System 10.0.0.0/16 (VPC-B) Peering-AB Custom Add a route with the CIDR block of VPC-B as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. rtb-VPC-B 10.0.0.0/24 Local System Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. 10.0.1.0/24 Local System 10.0.0.0/16 (VPC-A) Peering-AB Custom Add a route with the CIDR block of VPC-A as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. Table 2 VPC route table details
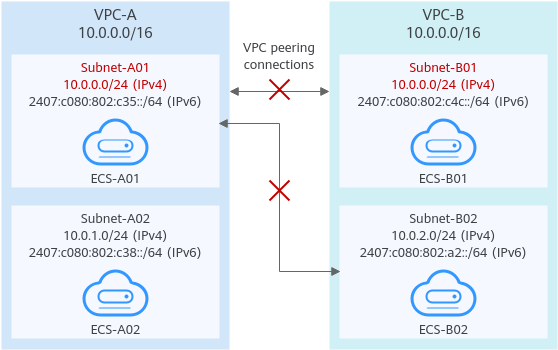
If two VPCs want to use their IPv6 CIDR blocks for communication by a VPC peering connection but the IPv4 CIDR blocks of the VPCs or subnets overlap, the connection is not usable.
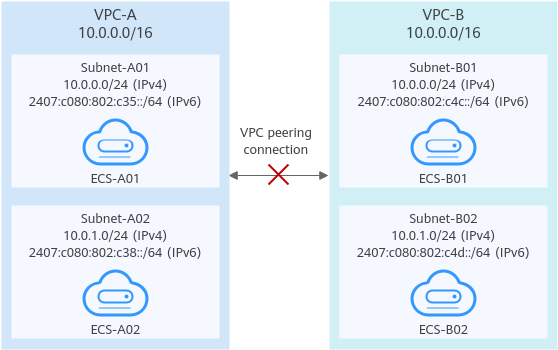
Two VPCs have overlapping CIDR blocks but some of their subnets do not overlap. VPC peering connections will not take effect in the following scenarios:
-
Connecting overlapping CIDR blocks of VPCs
As shown in Figure 3, if you create a VPC peering connection between VPC-A and VPC-B, the VPC peering connection will not take effect because the two VPCs have the same CIDR block.
-
Connecting overlapping subnets from different VPCs
If you create a VPC peering connection between Subnet-A01 and Subnet-B02, the route tables are shown in table below. In the rtb-VPC-B route table, the custom route for routing traffic from Subnet-B02 to Subnet-A01 and the local route have overlapping destinations. The local route has a higher priority and traffic will be forwarded within Subnet-B02 and cannot reach Subnet-A01.
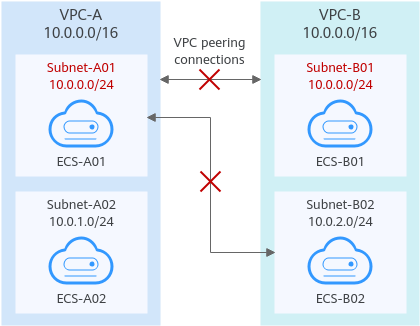
Route Table Destination Next Hop Route Type Description rtb-VPC-A 10.0.0.0/24 Local System Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. 10.0.1.0/24 Local System 10.0.2.0/24 (Subnet-B02) Peering-AB Custom Add a route with the CIDR block of Subnet-B02 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. rtb-VPC-B 10.0.0.0/24 Local System Local routes are automatically added for communications within a VPC. 10.0.2.0/24 Local System 10.0.0.0/24 (Subnet-A01) Peering-AB Custom Add a route with the CIDR block of Subnet-A01 as the destination and Peering-AB as the next hop. Table 3 VPC route table details
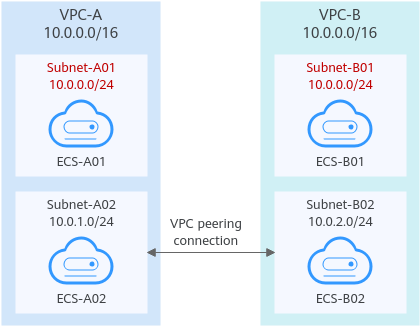
If the subnets connected by a VPC peering connection do not overlap, the connection will take effect. As shown in Figure 4, you can create a VPC peering connection between Subnet-A02 and Subnet-B02. In this case, the routes do not conflict and the VPC peering connection takes effect.
If two VPCs want to use their IPv6 CIDR blocks for communication by a VPC peering connection but the IPv4 CIDR blocks of the VPCs or subnets overlap, the connection is not usable.
-
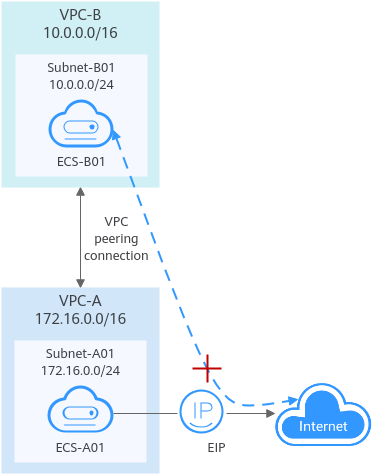
Invalid VPC Peering for Sharing an EIP
As shown in Figure 6, although VPC-A and VPC-B are peered and ECS-A01 in VPC-A has an EIP, ECS-B01 in VPC-B cannot access the Internet using the EIP bound to ECS-A01.