Aggregate CCE Logs with Promtail & Grafana Loki
This blueprint explains how to collect and centralize logs from Cloud Container Engine (CCE) using Promtail and Grafana Loki. It outlines the process of configuring Promtail as a log forwarder within Kubernetes and integrating it with Grafana Loki for efficient storage and visualization. By the end, you will have a unified and scalable logging setup that simplifies monitoring, troubleshooting, and operational insights across your CCE workloads.
Promtail has been officially deprecated and was transitioned into Long-Term Support (LTS) on February 13, 2025. The project continues to receive only essential security and critical bug fixes, with no new feature development. The LTS phase is planned to last approximately one year, ending on February 28, 2026, after which Promtail will enter its End-of-Life (EOL) phase on March 2, 2026. Once EOL is reached, maintenance, updates, and official support will cease entirely.
All new feature development and enhancements have moved to Grafana Alloy, which replaces Promtail as the actively maintained log collection agent.
If you are using Promtail, we are strongly recommending you migrate to Alloy or choose another forwarding solution, as Fluent-Bit that we already describe in another blueprint, Aggregate CCE Logs with Fluent Bit & Grafana Loki, how to integrate with Loki.
If you are currently using Promtail, it is strongly recommended to migrate to Grafana Alloy or adopt an alternative log forwarding solution such as Fluent Bit. The blueprint Aggregate CCE Logs with Fluent Bit & Grafana Loki provides detailed guidance on integrating Fluent Bit with Loki for a reliable and future-proof logging setup.
Grafana Loki serves as a log aggregation system optimized for scalability, availability, and cost efficiency. Drawing inspiration from Prometheus, Loki indexes only metadata through labels rather than the log content itself. It was introduced by Grafana Labs in 2018.
Loki uses Promtail to aggregate logs. Promtail is a logs collector agent that collects, labels, and ships logs to Loki. It runs on each Kubernetes node, using the same service discovery as Prometheus and supporting similar methods for labeling, transforming, and filtering logs before their ingestion to Loki.
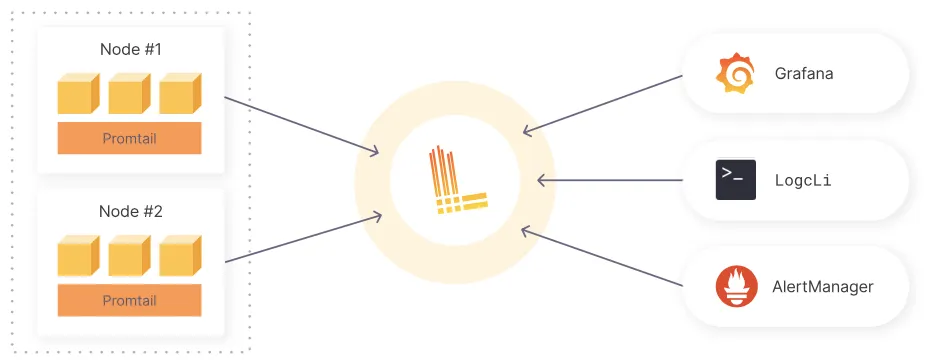
Loki groups log entries into streams and indexes them with labels, which reduces overall costs and the time between log entry ingestion and query availability.
Installing Grafana Loki
If you don’t already have a Grafana Loki instance running, you can set it up first before proceeding with log aggregation. The installation process is covered in detail in the companion blueprint Deploy Grafana Loki on CCE, which explains how to deploy Loki in microservices mode on Cloud Container Engine (CCE) with Open Telekom Cloud Object Storage (OBS) as the backend. Once Loki is up and running, you can continue here to install and configure Promtail and start collecting and centralizing logs from your CCE workloads.
Installing Promtail
Create a values file called values-promtail.yaml:
daemonset:
enabled: true
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 256Mi
tolerations:
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
- key: "node-role.kubernetes.io/master"
operator: "Exists"
effect: "NoSchedule"
config:
server:
http_listen_port: 3101
grpc_listen_port: 0
positions:
filename: /run/promtail/positions.yaml
clients:
- url: http://loki-gateway.monitoring.svc.cluster.local/loki/api/v1/push
batchwait: 1s
batchsize: 1048576
backoff_config:
min_period: 500ms
max_period: 5s
max_retries: 10
timeout: 10s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: kubernetes-pods
pipeline_stages:
- cri: {}
- json:
expressions:
msg: message | msg | log
level: level | severity
ts: ts | time | timestamp
- timestamp:
source: ts
format: RFC3339
action_on_failure: skip
- output:
source: msg
- labels:
level:
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- action: drop
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_phase]
regex: (Succeeded|Failed)
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
target_label: namespace
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
target_label: pod
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_container_name]
target_label: container
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app_kubernetes_io_name]
target_label: app
regex: (.+)
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app]
target_label: app
regex: (.+)
- action: replace
target_label: node
replacement: ${HOSTNAME}
# containerd/docker symlinked pod log path
- action: replace
source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_uid]
target_label: __path__
replacement: /var/log/pods/*$1/*.log
- action: labeldrop
regex: (pod_template_hash|controller_revision_hash)
rbac:
pspEnabled: false
serviceMonitor:
enabled: false
and deploy via Helm:
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade --install promtail grafana/promtail \
-f values-promtail.yaml \
-n monitoring --create-namespace
--reset-values
Installing Grafana (Optional)
For verification, we’ll install Grafana with Helm and include a simple demo dashboard to confirm that logs are reaching Loki. This lightweight setup is only for validation and smoke testing. For most production clusters, the recommended approach is to deploy the kube-prometheus-stack bundle, which provides Grafana together with Prometheus, Alertmanager, and curated dashboards, offering tighter integration and easier ongoing operations.
Create a values file called values-grafana.yaml:
adminUser: admin
persistence:
enabled: true
size: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
storageClassName: "csi-disk"
service:
enabled: true
type: ClusterIP
port: 80
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 256Mi
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
datasources:
datasources.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Loki
type: loki
access: proxy
url: http://loki-gateway.monitoring.svc.cluster.local
jsonData:
maxLines: 1000
derivedFields:
- datasourceUid: Loki
matcherRegex: "traceID=(\\w+)"
name: TraceID
url: "$${__value.raw}"
isDefault: true
editable: true
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: 'default'
orgId: 1
folder: ''
type: file
disableDeletion: false
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/default
dashboards:
default:
loki-logs:
gnetId: 15141
revision: 1
datasource: Loki
grafana.ini:
server:
root_url: "%(protocol)s://%(domain)s:%(http_port)s/"
analytics:
check_for_updates: true
check_for_plugin_updates: true
log:
mode: console
paths:
data: /var/lib/grafana/
logs: /var/log/grafana
plugins: /var/lib/grafana/plugins
provisioning: /etc/grafana/provisioning
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 472
runAsGroup: 472
fsGroup: 472
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
serviceMonitor:
enabled: false
rbac:
create: true
pspEnabled: false
serviceAccount:
create: true
autoMount: true
and deploy via Helm:
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade --install grafana grafana/grafana \
-f values-grafana.yaml \
-n monitoring --create-namespace \
--set "adminPassword=$(openssl rand -base64 24)" \
--reset values
Go to Grafana -> Dashboards and click the dashboard we provisioned as bundle with the Helm Chart Loki Kubernetes Logs:

💡 The Grafana admin password can be found in grafana secret in monitoring namespace.
⚠️ This Grafana installation and the provided dashboard are intended for demonstration purposes only.