Deploy Umami on CCE
In this blueprint we are going to set up Umami on Open Telekom Cloud's Cloud Container Engine (CCE), leveraging Kubernetes for scalability and flexibility. For the database backend, we will use the Zalando PostgreSQL Operator to provision and manage a PostgreSQL cluster within the CCE environment.
Prerequisites
We are going to need a CCE Cluster (its provisioning is out of the scope of this blueprint) and the zalando-postgres-operator. This operator automates the management of PostgreSQL clusters on Kubernetes, handling tasks like scaling, backups, and failover. It simplifies the deployment and maintenance of a highly available PostgreSQL database within the CCE cluster. Additionally we are going to need an Elastic Load Balancer in order to expose Umami.
Installing Zalando Postgres Operator
We are going to install the operator by using the provided Helm chart:
helm repo add postgres-operator-charts https://opensource.zalando.com/postgres-operator/charts/postgres-operator
helm repo update
helm install postgres-operator postgres-operator-charts/postgres-operator
Installing Umami
Provisioning a Database
As we priorly discussed, we are going to use zalando-postgres-operator in order to provision a PostgreSQL Cluster in CCE:
apiVersion: acid.zalan.do/v1
kind: postgresql
metadata:
labels:
application: umami
name: umami-psql
spec:
databases:
umami: umami
numberOfInstances: 1
postgresql:
version: "16"
parameters:
huge_pages: "false"
preparedDatabases:
umami:
defaultUsers: true
schemas:
data: {}
history:
defaultRoles: true
defaultUsers: false
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 500Mi
requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 100Mi
teamId: default
users:
admin:
- superuser
- createdb
umami: []
volume:
size: 1Gi
storageClass: csi-disk
kubectl apply -f umami-postgresql.yaml
Deploying Umami
Create the follow manifest:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: umami-web
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: umami-web
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: umami-web
spec:
containers:
- name: web
image: ghcr.io/umami-software/umami:postgresql-latest
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: PORT
value: '5000'
- name: DB_DATABASE
value: "umami"
- name: DB_HOST
value: umami-psql.docs-next.svc.cluster.local
- name: DB_PORT
value: '5432'
- name: DB_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: umami.umami-psql.credentials.postgresql.acid.zalan.do
key: username
- name: DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: umami.umami-psql.credentials.postgresql.acid.zalan.do
key: password
- name: DATABASE_URL
value: "postgres://$(DB_USERNAME):$(DB_PASSWORD)@$(DB_HOST):$(DB_PORT)/$(DB_DATABASE)"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
kubectl apply -f umami-web-deployment.yaml
A Kubernetes Secret with the name umami.umami-psql.credentials.postgresql.acid.zalan.do, containing the credentials of the umami database, will be automatically provisioned by the zalando-postgres-operator during the application of manifest umami-postgresql.yaml. The environmental variables DB_USERNAME & DB_PASSWORD are getting their values by referencing this Secret.
Creating an Elastic Load Balancer
Navigate to Network Console->Elastic Load Balancing and click Create Elastic Load Balancer. Choose to create Shared Load Balancer and choose New EIP so the new ELB is automatically bound to a new elastic IP:
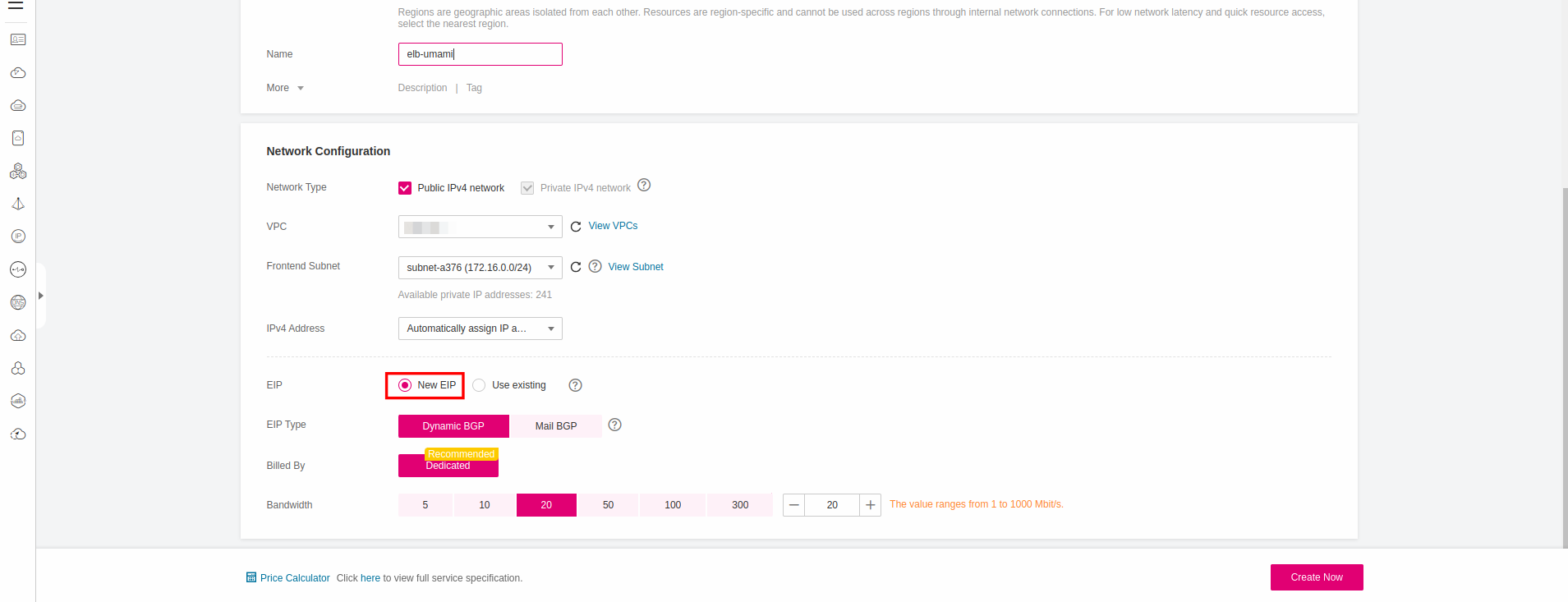
Write down the ID of the Elastic Load Balancer we are going to need it in the next steps.
Exposing Umami
Creating a Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: umami-web
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- protocol: TCP
name: umami
port: 5000
targetPort: 5000
selector:
app: umami-web
kubectl apply -f umami-service.yaml
If you are not planning to expose the service via an Ingress object, change the type to ClusterIP.
Creating an Ingress (optional)
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: umami-ingress
labels:
app: umami-web
annotations:
kubernetes.io/elb.class: union
kubernetes.io/elb.id: {value}
kubernetes.io/elb.port: 80
spec:
ingressClassName: cce
rules:
- host: umami.example.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: umami-web
port:
number: 5000
path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
- Replace the placeholder
{value}of annotation kubernetes.io/elb.id with the ID of the Elastic Load Balancer we created before. - If the Elastic Load Balancer you created was a shared one then the annotation kubernetes.io/elb.class should have the value
union. - Replace
umami.example.comin host, with the FQDN of yours.
kubectl apply -f umami-ingress.yaml
Verification
Open in a browser the address: http://ELB_EIP and you should now land at the logon page of Umami:
Umami uses admin/umami as default credentials. Change them immediatelly after you log in!