How Do Replica Sets Achieve High Availability and Read/Write Splitting?
DDS replica set instances can store multiple duplicates to ensure data high availability and support the automatic switch of private IP addresses to ensure service high availability. To enhance the read and write performance of your client for connecting to the instance, you can use your client to read different data copies. You need to connect to replica set instances using HA connection addresses. You can also configure read/write splitting. Otherwise, the high availability and high read performance of replica set instances cannot be guaranteed.
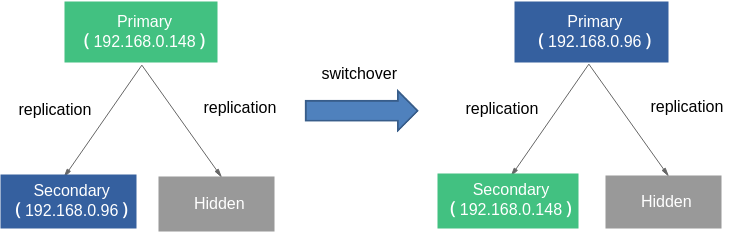
The primary node of a replica set instance is not fixed. If the instance settings are changed, or the primary node fails, or primary and secondary nodes are switched, a new primary node will be elected and the previous one becomes a secondary node. The following figure shows the process of a switchover.
Connecting to a Replica Set Instance (HA)
A DDS replica set consists of the primary, secondary, and hidden nodes. The hidden node is invisible to users. Read/Write splitting and HA can be realized only when you connect to the IP addresses and ports of the primary and secondary nodes of the replica set at the same time (in HA mode).
The following describes how to use URL and Java to connect to an instance in HA mode.
Method 1: Using a URL
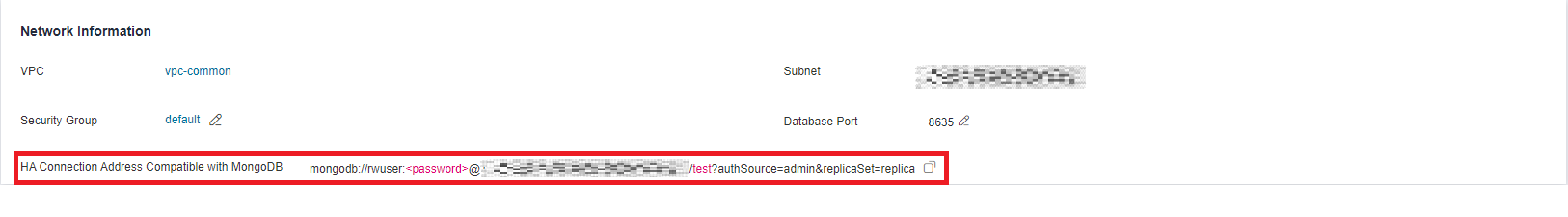
On the Instances page, click the instance name. The Basic Information page is displayed. Choose Connections. Click the Private Connection tab and obtain the connection address of the current instance from the Private HA Connection Address field.
Example:
mongodb://rwuser:\*\*\*\*@**_192.168.0.148:8635,192.168.0.96:8635_**/test?authSource=admin&replicaSet=replica
In the preceding URL, 192.168.0.148:8635 and 192.168.0.96:8635 are the IP addresses and ports of the primary and secondary nodes, respectively. If you use this address, the connection between your client and the instance can be ensured even when a primary/standby switchover occurs. In addition, using multiple IP addresses and port numbers can enhance the read and write performance of the entire database.
Method 2: Using a Java Driver
Sample code:
MongoClientURI connectionString = new MongoClientURI("mongodb://rwuser:****@192.168.0.148:8635,192.168.0.96:8635/test?authSource=admin&replicaSet=replica"); MongoClient client = new MongoClient(connectionString);
MongoDatabase database = client.getDatabase("test");
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("mycoll");
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| rwuser:**** | Username and password for starting authentication |
| 192.168.0.148:8635,192.168.0.96:8635 | IP addresses and ports of the primary and secondary nodes in a replica set instance |
| test | Name of the database to be connected |
| authSource=admin | Database username for authentication |
| replicaSet=replica | Name of the replica set instance type |
Table 1" Parameter description
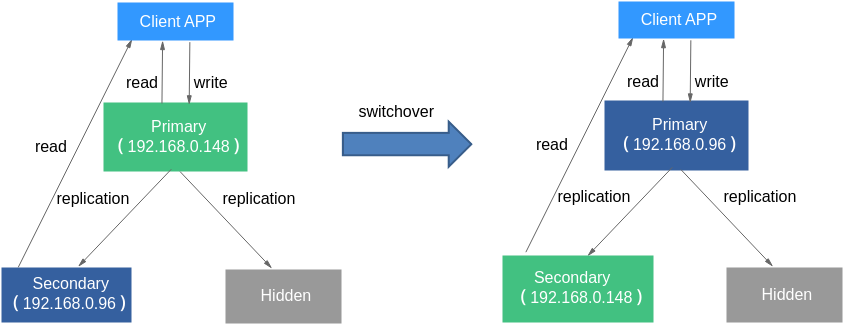
Connecting to a Replica Set Instance
This is not recommended!
Using the Connection Address:
mongodb://rwuser:\*\*\*\*@**_192.168.0.148:8635_**/test?authSource=admin&replicaSet=replica
In the preceding URL, 192.168.0.148:8635 is the IP address and port number of the current primary node. If a switchover occurs or the primary node is changed, the client fails to connect to the replica set instance because the IP address and port of the newly elected primary node is unknown. As a result, the database service becomes unavailable. In addition, read and write operations can only be performed on a fixed primary node, so the read and write performance cannot be improved by adding nodes.
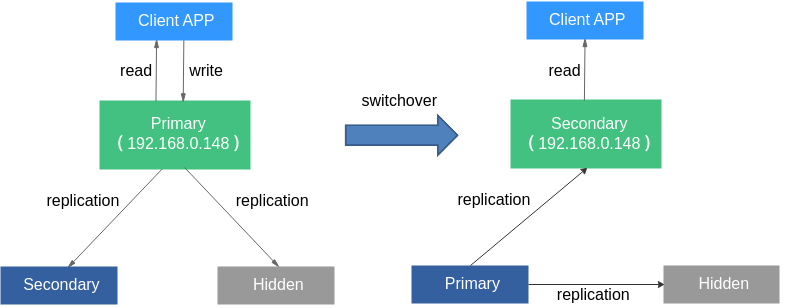
Read/Write Splitting
The following HA connection address is used as an example to describe how to connect to a DDS replica set instance:
mongodb://rwuser:<password>@192.168.xx.xx:8635,192.168.xx.xx:8635/test?
authSource=admin&replicaSet=replica&readPreference=secondaryPreferred
The database account is rwuser, and the database is admin.
After the DB instance is connected, read requests are preferentially sent to the secondary node to implement read/write splitting. If the relationship between the primary and secondary nodes changes, write operations are automatically switched to the new primary node to ensure high availability of DDS.