Auto Scaling Based on ELB Monitoring Metrics with KEDA
This article demonstrates how to implement auto scaling using KEDA (Kubernetes Event-driven Autoscaling) with ELB monitoring metrics.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding with this guide, make sure the environment setup described in this section has been completed. You should also be familiar with the basic concepts of KEDA, particularly the ScaledObject resource.
Solution Design
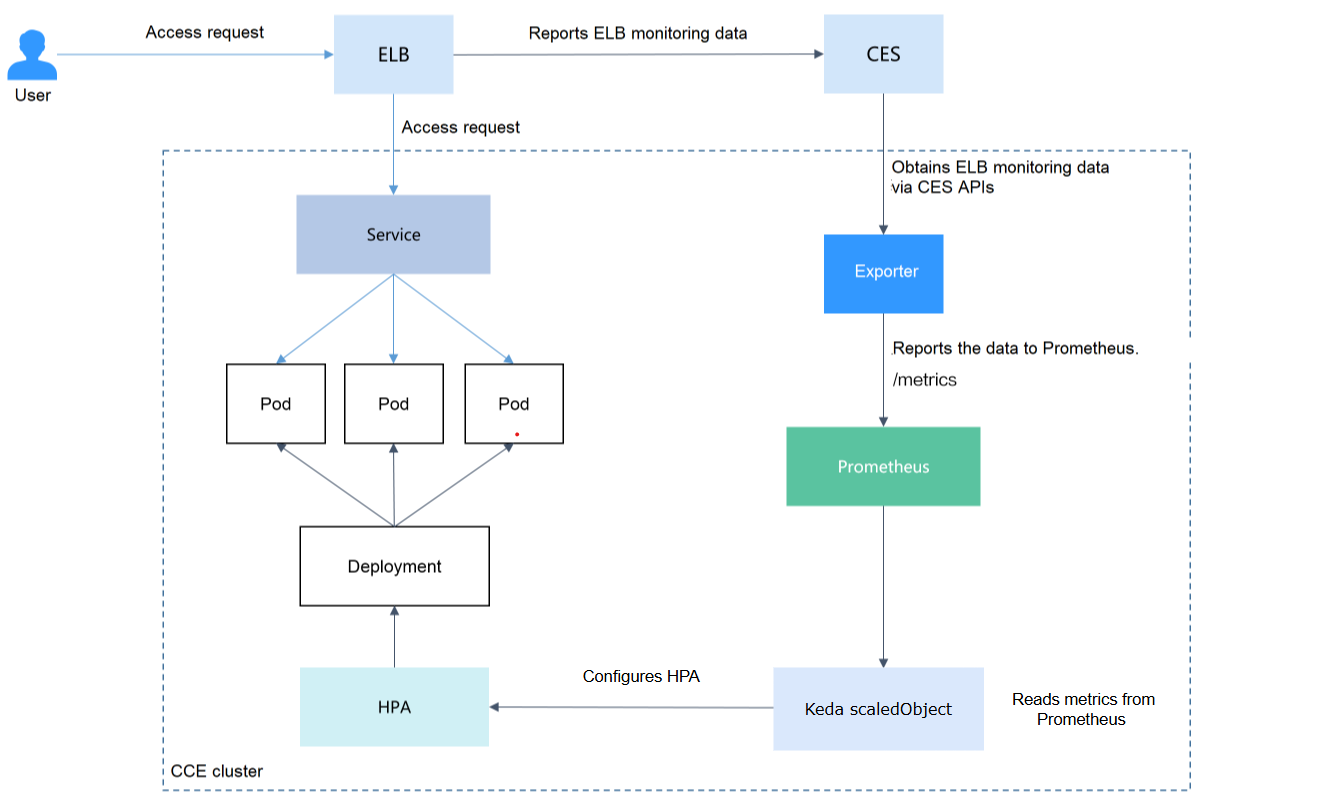
This section outlines an auto scaling approach that leverages ELB monitoring metrics through KEDA. Unlike traditional scaling methods based on CPU or memory usage, using ELB QPS data enables faster and more precise scaling decisions, while also supporting advanced capabilities such as scaling workloads down to zero. KEDA functions as a mediator between external metric sources and Kubernetes, translating those metrics into scaling actions in real time. The core of this solution is configuring a ScaledObject to use ELB monitoring data as the metric source for automatic scaling decisions.
Key Benefits of KEDA over HPA
- Scale to/from Zero: KEDA can reduce workloads to zero replicas during periods of inactivity, helping to optimize resource usage and lower costs.
- Multiple Scalers: It supports combining multiple scaling triggers, such as CPU utilization, custom metrics, or external API data.
Installing KEDA
Installing KEDA with Helm
On a bastion host, install KEDA using Helm:
helm repo add kedacore https://kedacore.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm install keda kedacore/keda --namespace keda --create-namespace
Then verify that KEDA is running correctly; you should observe both the KEDA operator and the metrics server pods in a running state.
kubectl get pods -n keda
Creating a ScaledObject
Once the exporter starts sending data to Prometheus, you can define a ScaledObject policy to enable automatic scaling based on those metrics.
Basic ScaledObject Configuration
Create a ScaledObject custom resource that uses inbound ELB traffic as the scaling trigger. When the metric m4_ncps (new connections per second) surpasses 100, the nginx Deployment will automatically scale out.
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
name: nginx
minReplicaCount: 1
maxReplicaCount: 10
cooldownPeriod: 300
triggers:
- type: prometheus
metadata:
serverAddress: http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090
threshold: '100'
query: opentelekomcloud_sys_elb_m4_ncps{lbaas_instance_id="INSTANCE_ID"} # Replace INSTANCE_ID with your ELB instance ID
activationThreshold: '20'
The ScaledObject must be deployed in the same namespace as the target Deployment.
Advanced ScaledObject Configuration
In production environments, more advanced configurations may be required. For instance, you can combine multiple metrics, such as new and concurrent connections, to drive scaling decisions. Parameters like pollingInterval and cooldownPeriod can also be adjusted to fine-tune how quickly the system reacts to changing traffic patterns.
apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
kind: ScaledObject
metadata:
name: nginx
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
name: nginx
minReplicaCount: 1
maxReplicaCount: 20
pollingInterval: 15 # Check metrics every 15 seconds
cooldownPeriod: 180 # Wait 3 minutes before scaling down
advanced:
scalingModifiers:
target: "100"
activationTarget: "20"
metricType: "AverageValue"
# Combine new connections and concurrent connections
formula: "new_connections * 2 + concurrent_connections * 0.1"
triggers:
- type: prometheus
name: new_connections
metadata:
serverAddress: http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090
query: opentelekomcloud_sys_elb_m4_ncps{lbaas_instance_id="INSTANCE_ID"} # Replace INSTANCE_ID with your ELB instance ID
threshold: '1' # Will be overridden by scalingModifiers
- type: prometheus
name: concurrent_connections
metadata:
serverAddress: http://prometheus-kube-prometheus-prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090
query: opentelekomcloud_sys_elb_m1_cps{lbaas_instance_id="INSTANCE_ID"} # Replace INSTANCE_ID with your ELB instance ID
threshold: '1' # Will be overridden by scalingModifiers
Applying the ScaledObject
Apply the ScaledObject configuration:
kubectl apply -f nginx-scaledobject.yaml
Testing the Scaling
After creating the ScaledObject, run a load test on the workload by sending traffic through the ELB. KEDA will monitor the configured metric and determine whether scaling actions are needed based on the defined thresholds. You can observe the scaling activity:
kubectl get scaledobject nginx -w
# KEDA creates HPA objects internally
kubectl get hpa -w